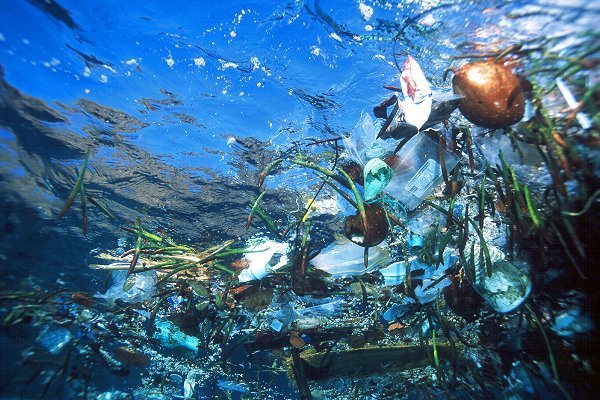
With approximately 250 000 marine species, the ocean is a vast reservoir of biodiversity and an abundant biological resource of natural polymers. The wide variety, renewable nature, tunable physicochemical and structural behavior and appealing biological properties make these marine biopolymers particularly attractive to the scientific community and numerous industrial sectors. As raw materials, they offer novel opportunities for the development of bio-based materials in response to recent demands for biodegradable plastic materials to lower plastic pollution in marine ecosystems. The biodegradation of marine biopolymers and biopolymer-based materials depends on marine environmental conditions such as temperature, pH and in particular microbial population. Marine microorganisms producing biopolymer-degrading enzymes (i.e., hydrolases, lyases, oxidoreductases) are well studied, nonetheless the biodegradation processes of marine biopolymers-based materials in the marine/aquatic environment need further investigation. This review describes various biodegradation parameters and mechanisms of the degradation of marine biopolymers in the marine environment. It also puts emphasis on the marine microorganisms and the corresponding enzymes that catalyze the degradation of different marine biopolymers. Finally, it focuses on the few studies on biodegradation of emerging bio-based materials in aquatic ecosystems (Samalens et al., 2022).
Personal notes:
Bioplastic experiments have been conducted to obtain information on the degradation process on land and in the marine ecosystem. The degradation of polymers depends entirely on external factors, and it is based on the surrounding environment. Therefore, the analysis must be performed under specific conditions which limit the development of these experiments. Chitin is one of the most abundant biopolymers after cellulose (Samalens et al., 2022). An essential aspect of this polysaccharide is that several unicellular organisms in the marine ecosystem synthesize it. As a result, it has become one of the most used raw materials to manufacture biobased materials. It is a well-known material and has also been used in different applications, like tissue engineering.
Samalens, F., Thomas, M., Claverie, M., Castejon, N., Zhang, Y., Pigot, T., Blanc, S., & Fernandes, S. C. (2022). Progresses and future prospects in biodegradation of marine biopolymers and emerging biopolymer-based materials for Sustainable Marine Ecosystems. Green Chemistry, 24(5), 1762–1779. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1gc04327g