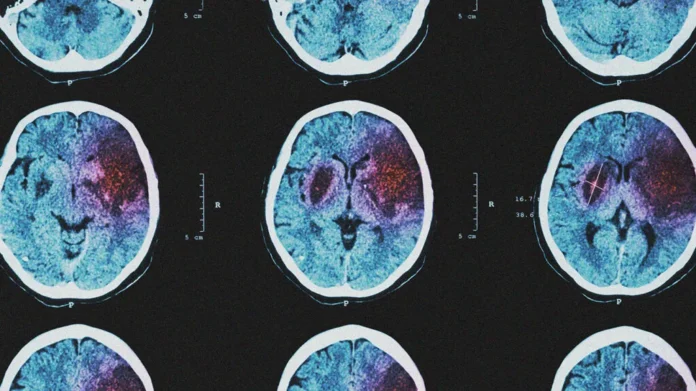
Stroke is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. Approximately 60% of stroke survivors require rehabilitation which might take from months to years depending on the size of the brain injury and the particular brain circuits that are damaged. Rehabilitation doesn’t reverse brain damage but it definitely helps stroke survivors achieve the best long-term outcome since the brain has the ability to rewire its circuits after a stroke which leads to a degree of improved function.
A stroke can cause multiple types of disabilities; problems with thinking and memory, emotional disturbances, problems using or understanding language, sensory disturbances including pain, and paralysis or problems controlling movement (motor control); damage to certain brain cells and nerves causes problems with movement and sensation including paralysis on one side of the body, which is called hemiplegia, or weakness on one side, which is called hemiparesis.
Rehabilitation begins in the hospital once the condition has stabilized, often two day after the stroke. The patient goes through therapy that helps him with movement and a range of exercises to overcome any paralysis or weakness for him to be able to perform basic movements with or without the help of others. Rehabilitation includes a team of specialists such as, Physicians, Rehabilitation nurses, Physical Therapists, Occupational Therapists, Therapeutic recreation specialists, Speech-language specialists, Vocational therapists, Social workers, and Psychologists.
Reflection/Analysis:
As the patient survive the stroke the rehabilitation stage begins immediately, which puts the patient under a lot of pressure including treatment, recovery, rehabilitation, etc. This article helps fully understand the reasons a stroke is caused, the steps a stroke survivor has to go through, and the post stroke life and routine. Helping guide the patients and understanding their experience is a crucial part of coming up with more solutions aiming towards a better post-stroke long-term recovery.